Kitchen appliances: selection, care and energy efficiency
Kitchen appliances shape how a home functions: they save time, affect running costs and influence kitchen design. Choosing and maintaining appliances requires balancing capacity, energy use, installation needs and long-term reliability. This article explains common appliance types, selection criteria, energy considerations, installation and maintenance advice, and how to source local services or responsibly replace units.
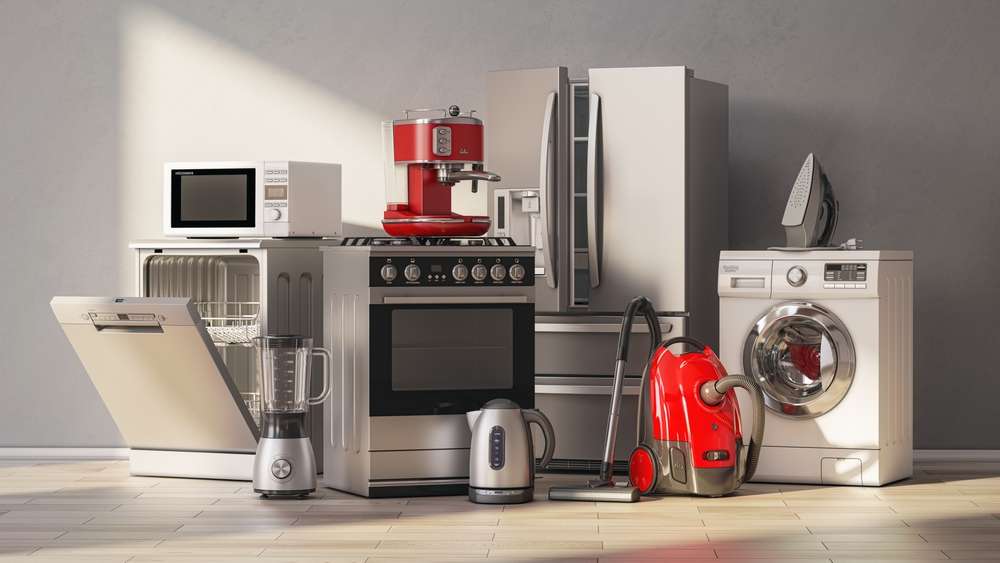

What types of kitchen appliances exist?
Kitchen appliances fall into several categories: cooking (ovens, hobs, microwaves), refrigeration (fridges, freezers), dishwashing, food preparation (blenders, mixers, food processors) and small countertop appliances (kettles, toasters, coffee machines). Built-in appliances integrate with kitchen units and often require specific dimensions and ventilation. Freestanding items are more flexible for placement. Knowing the category helps narrow choices according to daily routines, household size and available space.
How to choose appliances for your kitchen
Start by measuring available space and checking utility connections (electric, gas, water). Think about capacity: larger households usually need bigger fridges and dishwashers, while single occupants may prefer compact models. Consider layout and workflow—place appliances to minimise walking between preparation, cooking and cleaning zones. Look at control types, safety features, noise levels and warranties. Read manufacturer specifications for power consumption and installation requirements to ensure compatibility with your kitchen’s electrics and plumbing.
Energy use and efficiency considerations
Energy efficiency affects both running costs and environmental impact. Check official energy labelling and compare annual energy consumption figures (kWh/year) for refrigeration and dishwashing appliances. Oven and hob efficiency depends on insulation and technology—induction hobs usually use less energy than traditional electric coil hobs. For appliances with heating elements, conscious use (full loads for dishwashers, avoiding preheating when unnecessary) reduces energy use. Consider long-term costs as well as purchase price when evaluating eco credentials.
Installation and planning for appliances
Installation often requires professional assessment: gas appliances must be installed by a qualified engineer, and induction or high-power electric ovens may need specific fuse ratings. Ventilation is critical for some built-in units to prevent overheating and maintain performance. Plan delivery access and ensure there is adequate clearance for doors and drawers. If you live in a flat or older property, check whether building restrictions or communal regulations affect installation. For complex fits, consult a kitchen installer or electrician from local services.
Maintenance, repairs and finding local services
Regular maintenance extends appliance life: clean filters in extractor hoods and dishwashers, defrost freezers as recommended, and avoid abrasive cleaners on seals. Keep user manuals for troubleshooting and follow prescribed service schedules. If repairs are needed, look for authorised repair centres or technicians through local services and check for spare parts availability from manufacturers. When booking repairs, confirm fix warranties and whether the technician is certified for gas or electrical work, depending on the appliance.
Responsible replacement and disposal
When replacing appliances, compare the energy rating of the new unit to the old one to estimate potential savings. Many retailers and local councils offer take-back or recycling services for old appliances; using these pathways helps manage hazardous components like refrigerants and electronic waste. If selling or donating working appliances, ensure they are clean and in safe working order. For end-of-life units, ask local services about recycling centres or scheduled bulky waste collections in your area to meet environmental regulations.
Conclusion
Selecting the right kitchen appliances combines practical measurements, an understanding of household needs, attention to energy performance and planning for installation and maintenance. Regular care and informed choices can reduce operating costs and extend service life, while using authorised local services and responsible disposal routes minimises environmental impact.